The UC Riverside team is tasked to deploy instrumentation on the aircraft to measure aerosol properties, including cloud condensation nuclei (CCN), refractory black carbon (rBC), and the aerosol size distribution. On Tuesday November 7, 2023 we arrived at long last in Boulder to work on integrating our instruments into the C-130 aircraft. Our first task was to make modifications to the rack so it would pass FAA inspection. The NCAR machine shop added additional braces to better secure the instruments against strong forces during takeoff and landing. We made small modifications to the data acquisition box to increase resistance against vibration.
|
|
|

|
|
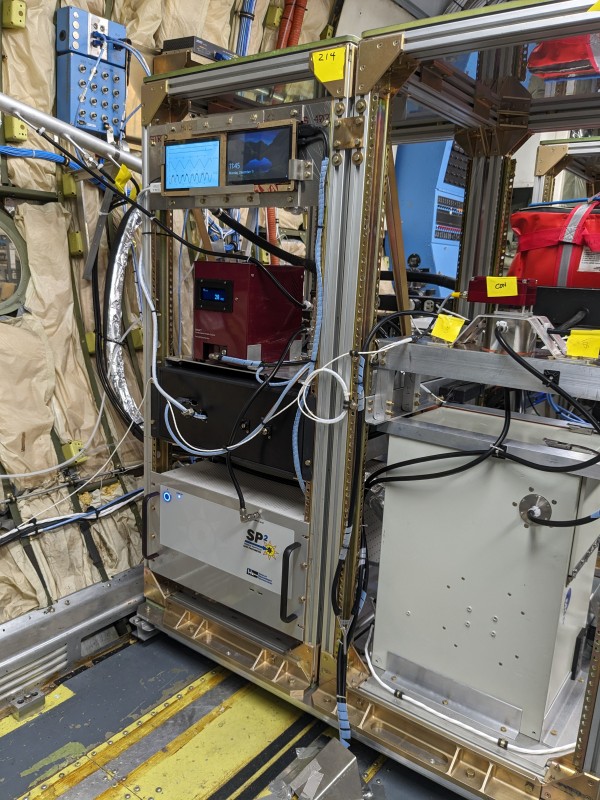
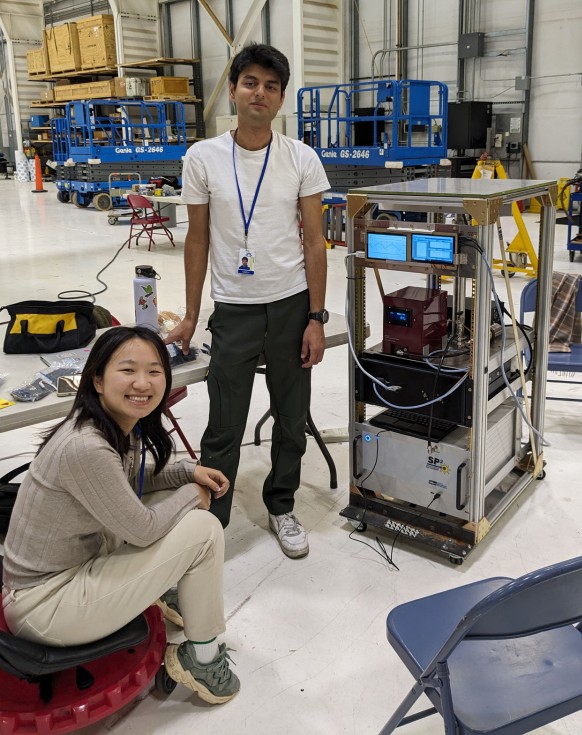
Photo. Lintong Cai and Sunandan Mahant working on the rack that houses the scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) to measure the particle size distribution and the thesingle particle soot photometer (SP2) to measure refractory black carbon.
|
A critical test is whether the instruments will operate at a pressure difference. During flight, the cabin is pressurized, while the sample flowing through the instrument is at reduced pressure. Thus, after every modification we check the instruments for leaks.
|
|
|

|
|
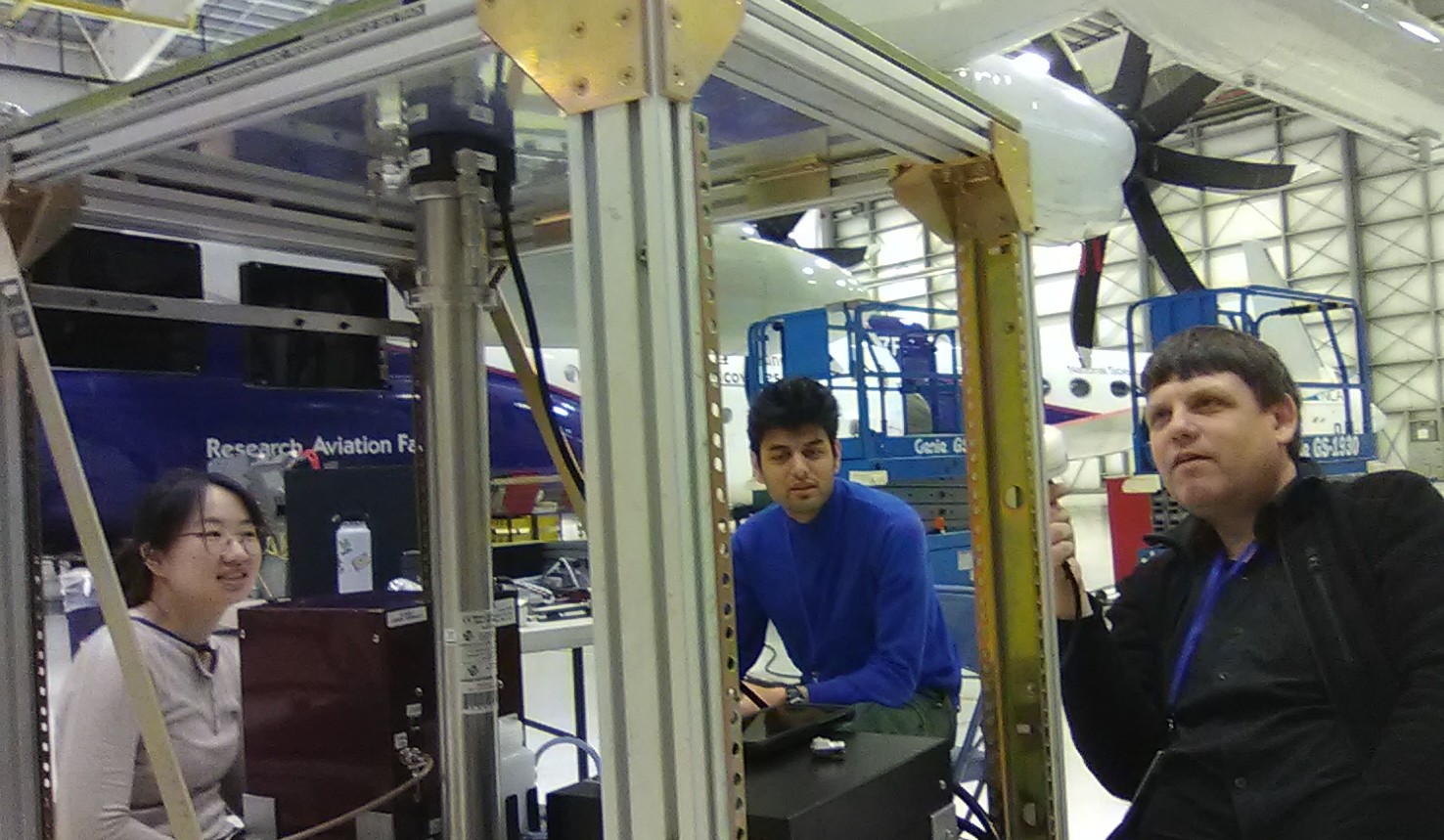
Photo. Lintong Cai and Sunandan Mahant and Markus Petters hunting for leaks in the SMPS when operating under low pressure.
|
After the we were approved, the instruments were installed in the aircraft cabin and tested prior to our first test flights.
|
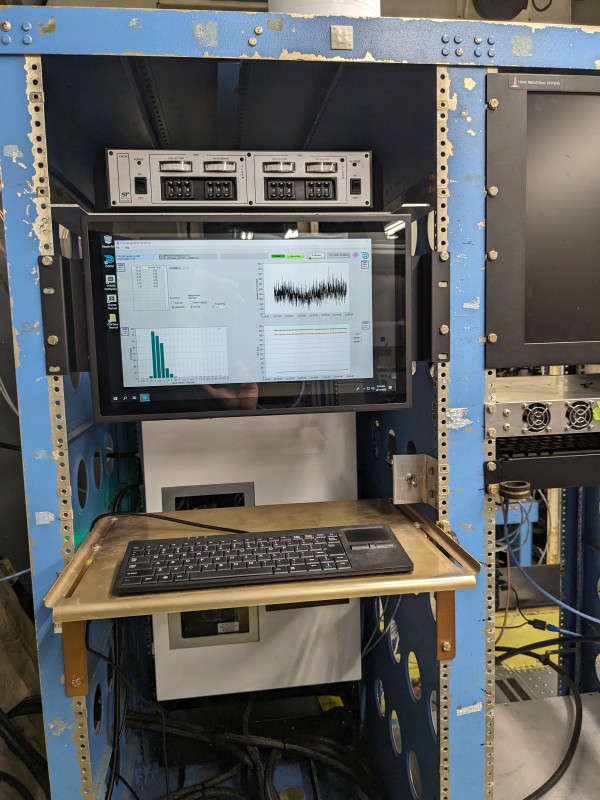
Photo. Left: Installed cloud condensation nuclei instrument (CCN). Right: Installed scanning mobility particle sizer and single particle soot photometer.
|
The University of Wyoming team is tasked to measure the cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) and the aerosol size distribution. To this end, two instruments, a static cloud condensation nuclei counter and Ultra-High Sensitivity Aerosol Spectrometer (UHSAS) are added to the aircraft.
|
|
|

|
|
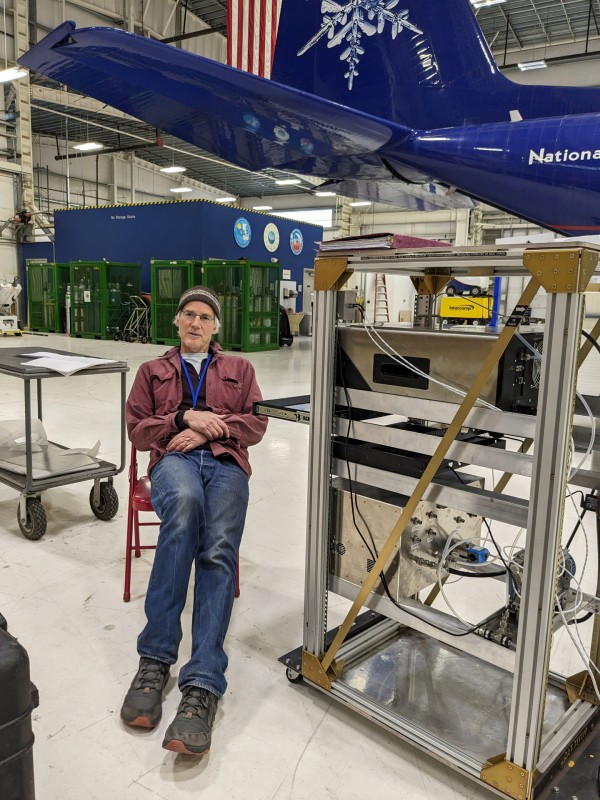
Photo. Jefferson Snider working on the rack that houses the University of Wyoming CCN instrument and the University of Wyoming Ultra-High Sensitivity Aerosol Spectrometer.
|
To sample inside the aircraft fuselage, air is brought inside via an inlet system. The University of Riverside cloud condensation nuclei counter, the University of Wyomming cloud condensation nuclei counter, and the University of Wyoming ultra-high sensitivity aerosol spectrometer share an HIMIL inlet on the left side of the plane.
|
|
|

|
|
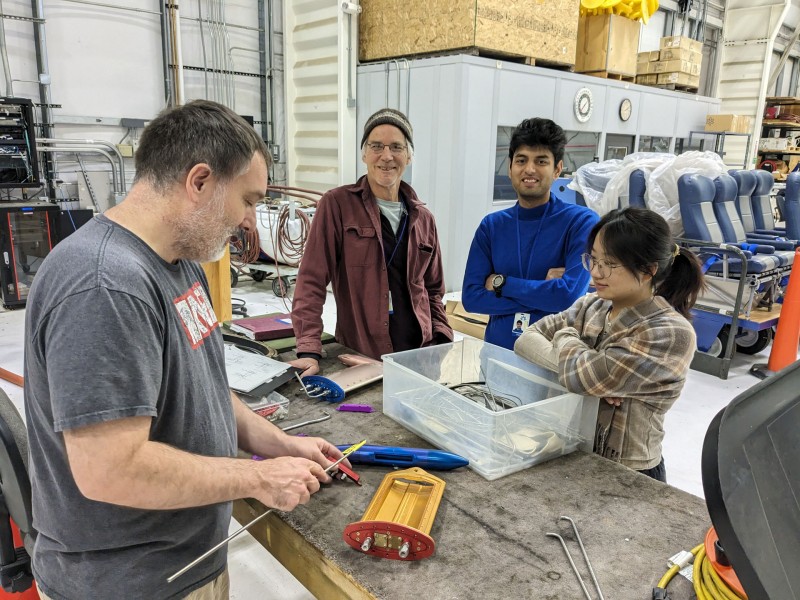
Photo. David Albee (NCAR), Jefferson Snider, Sunandan Mahant, and Lintong Cai are working together to decide on the configuration of the HIMIL inlet that will be used to bring sample air into the aircraft.
|